|
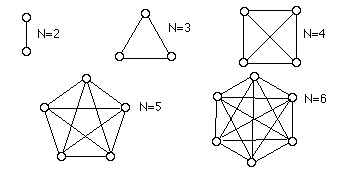
A fully connected network is one where each host on the network has a direct wire to every other host. This is okay for 2, 3, or even 4 hosts, but soon it begins to escalate. If there are N hosts, then the number of wires needed for a fully connected network is (N2-N)/2, which for all intents is N2, which is bad. If one more computer is added, N wires must be added. If the size of the network doubles, the number of wires goes up by 4. Fig. 23.11.1 shows fully connected networks of various sizes. |