|
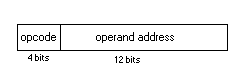
The instruction register is divided into two sections conceptually, but not physically. Fig. 7.1.4 shows this division. The first four bits are commonly called the opcode, short for operation code. The contents of these bits form a 4-bit binary number which tells the control unit which instruction to perform. The remaining 12 bits form the operand, which is either a 12-bit binary number or an address. |